- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录1194 > ADT7467BBZEVB (ON Semiconductor)BOARD EVALUATION FOR ADT7467
�� �
�
ADT7467�
�?� Worst-case� Altitude�
�A� computer� can� be� operated� at� different� altitudes.� The�
�altitude� affects� the� relative� air� density,� which� alters� the�
�effectiveness� of� the� fan� cooling� solution.� For� example,�
�comparing� 40� ?� C� air� temperature� at� 10,000� ft.� to� 20� ?� C�
�air� temperature� at� sea� level,� relative� air� density� is�
�misaligned.� Too� much� or� too� little� thermal� grease� might�
�be� used,� or� variations� in� application� pressure� for�
�thermal� interface� material� could� affect� the� efficiency� of�
�the� thermal� solution.� Accounting� for� manufacturing�
�variations� in� every� system� is� difficult;� therefore,� the�
�system� must� be� designed� for� worst-case� conditions.�
�T� TIM�
�q� CTIM�
�?�
�increased� by� 40%.� This� means� that� at� a� given�
�temperature,� the� fan� can� spin� 40%� slower� and� make� less�
�noise� at� sea� level� than� it� can� at� 10,000� ft.�
�Worst-case� Fan�
�Due� to� manufacturing� tolerances,� fan� speeds� in� RPM�
�are� normally� quoted� with� a� tolerance� of� ?� 20%.� The�
�designer� should� assume� that� the� fan� RPM� is� 20%� below�
�tolerance.� This� translates� to� reduced� system� airflow� and�
�elevated� system� temperature.� Note� that� a� difference� of�
�20%� in� the� fans’� tolerance� can� negatively� impact�
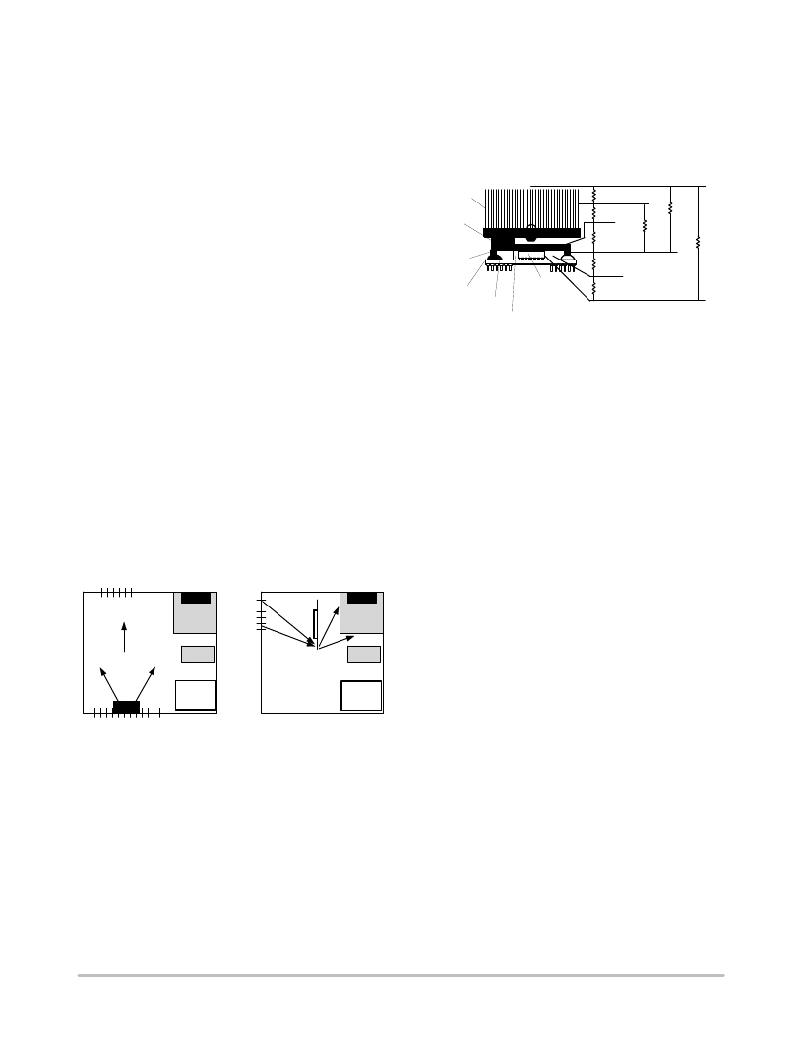
�Heat� Sink�
�Thermal�
�Interface�
�Material�
�Integrated�
�Heat�
�Spreader�
�Processor�
�Substrate�
�Epoxy�
�Thermal� Interface� Material�
�q� SA� T� S�
�q� TIMS�
�q� TIMC�
�q� JTIM�
�T� A�
�q� CS�
�T� C�
�T� TIM�
�T� J�
�q� CA�
�q� JA�
�system� acoustics� because� the� fans� run� faster� and�
�Figure� 50.� Thermal� Model�
�Fan�
�Fan�
�Vents�
�?�
�generate� more� noise.�
�Worst-case� Chassis� Airflow�
�The� same� motherboard� can� be� used� in� a� number� of�
�different� chassis� configurations.� The� design� of� the�
�chassis� and� the� physical� location� of� fans� and�
�components� determine� the� system� thermal�
�characteristics.� Moreover,� for� a� given� chassis,� the�
�addition� of� add-in� cards,� cables,� and� other� system�
�configuration� options� can� alter� the� system� airflow� and�
�reduce� the� effectiveness� of� the� system� cooling� solution.�
�The� cooling� solution� can� also� be� inadvertently� altered�
�by� the� end� user.� (For� example,� placing� a� computer�
�against� a� wall� can� block� the� air� ducts� and� reduce� system�
�airflow.)�
�Vents�
�I/O� Cards�
�I/O� Cards� Power� Power�
�Supply� Supply�
�Although� a� design� usually� accounts� for� such� worst-case�
�conditions,� the� system� is� almost� never� operated� at�
�worst-case� conditions.� An� alternative� to� designing� for� the�
�worst� case� is� to� use� the� dynamic� T� MIN� control� function.�
�Dynamic� T� MIN� Control� Overview�
�Dynamic� T� MIN� control� mode� builds� on� the� basic�
�automatic� fan� control� loop� by� adjusting� the� T� MIN� value�
�based� on� system� performance� and� measured� temperature.�
�Therefore,� instead� of� designing� for� the� worst� case,� the�
�system� thermals� can� be� defined� as� operating� zones.�
�ADT7467� can� self-adjust� its� fan� control� loop� to� maintain�
�either� an� operating� zone� temperature� or� a� system� target�
�temperature.� For� example,� users� can� specify� that� the� ambient�
�temperature� in� a� system� be� maintained� at� 50� ?� C.� If� the�
�temperature� is� below� 50� ?� C,� the� fans� may� not� run� or� may� run�
�very� slowly.� If� the� temperature� is� higher� than� 50� ?� C,� the� fans�
�may� throttle� up.�
�The� challenge� presented� by� any� thermal� design� is� finding�
�Good� CPU� Airflow�
�Fan�
�CPU�
�Drive�
�Bays�
�Poor� CPU�
�Airflow�
�CPU�
�Drive�
�Bays�
�the� right� settings� to� suit� the� system’s� fan� control� solution.�
�This� can� involve� designing� for� the� worst� case,� followed� by�
�weeks� of� system� thermal� characterization,� and� finally� fan�
�acoustic� optimization� (for� psychoacoustic� reasons).�
�Poor� Venting� =�
�Vents�
�Good� Venting� =� Good� Air� Exchange� Poor� Air� Exchange�
�Figure� 49.� Chassis� Airflow� Issues�
�?� Worst-case� Processor� Power� Consumption�
�Designing� for� worst-case� CPU� power� consumption� can�
�result� in� a� processor� becoming� overcooled,� generating�
�excess� system� noise.�
�?� Worst-case� Peripheral� Power� Consumption�
�The� tendency� is� to� design� to� data� sheet� maximums� for�
�peripheral� components� (again� overcooling� the� system).�
�?� Worst-case� Assembly�
�Every� system� is� unique� because� of� manufacturing�
�variations.� Heat� sinks� may� be� loose� fitting� or� slightly�
�Optimizing� the� automatic� fan� control� mode� involves�
�characterizing� the� system� to� determine� the� best� T� MIN� and�
�T� RANGE� settings� for� the� control� loop� and� the� PWM� MIN� value�
�that� produces� the� quietest� fan� speed� setting.� Using� the�
�ADT7467� dynamic� T� MIN� control� mode,� however,� shortens�
�the� characterization� time� and� alleviates� tweaking� the� control�
�loop� settings� because� the� device� can� self-adjust� during�
�system� operation.�
�Dynamic� T� MIN� control� mode� is� operated� by� specifying� the�
�operating� zone� temperatures� required� for� the� system.�
�Associated� with� this� control� mode� are� three� operating� point�
�registers,� one� for� each� temperature� channel.� This� allows� the�
�system� thermal� solution� to� be� broken� down� into� distinct�
�thermal� zones.� For� example,� CPU� operating� temperature� is�
�70� ?� C,� VRM� operating� temperature� is� 80� ?� C,� and� ambient�
�http://onsemi.com�
�32�
�发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
ADT7468ZEVB
BOARD EVAL FOR ADT7468
ADT7473ZEVB
BOARD EVALUATION FOR ADT7473
ADT7475EBZEVB
BOARD EVALUATION FOR ADT7475
ADT7476EBZEVB
BOARD EVALUATION FOR ADT7476
ADT7490ZEVB
BOARD EVALUATION FOR ADT7490
ADZS-21262-1-EZEXT
BOARD DAUGHTER FOR ADSP-21262
ADZS-BF-EZEXT-1
BOARD DAUGHTER ADSP-BF533/561KIT
ADZS-BFAV-EZEXT
BOARD DAUGHT ADSP-BF533,37,61KIT
相关代理商/技术参数
ADT7468
制造商:AD 制造商全称:Analog Devices 功能描述:dBCool⑩ Remote Thermal Controller and Voltage Monitor
ADT7468ARQ
功能描述:IC REMOTE THERMAL CTRLR 24-QSOP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热管理 系列:dBCool® 标准包装:1 系列:- 功能:温度监控系统(传感器) 传感器类型:内部和外部 感应温度:-40°C ~ 125°C,外部传感器 精确度:±2.5°C 本地(最大值),±5°C 远程(最大值) 拓扑:ADC,比较器,寄存器库 输出类型:2 线 SMBus? 输出警报:无 输出风扇:无 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 125°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:SOT-23-8 供应商设备封装:SOT-23-8 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:296-22675-6
ADT7468ARQ-REEL
功能描述:IC REMOTE THERMAL CTRLR 24-QSOP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热管理 系列:dBCool® 标准包装:1 系列:- 功能:温度监控系统(传感器) 传感器类型:内部和外部 感应温度:-40°C ~ 125°C,外部传感器 精确度:±2.5°C 本地(最大值),±5°C 远程(最大值) 拓扑:ADC,比较器,寄存器库 输出类型:2 线 SMBus? 输出警报:无 输出风扇:无 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 125°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:SOT-23-8 供应商设备封装:SOT-23-8 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:296-22675-6
ADT7468ARQ-REEL7
功能描述:IC REMOTE THERMAL CTRLR 24-QSOP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热管理 系列:dBCool® 标准包装:1 系列:- 功能:温度监控系统(传感器) 传感器类型:内部和外部 感应温度:-40°C ~ 125°C,外部传感器 精确度:±2.5°C 本地(最大值),±5°C 远程(最大值) 拓扑:ADC,比较器,寄存器库 输出类型:2 线 SMBus? 输出警报:无 输出风扇:无 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 125°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:SOT-23-8 供应商设备封装:SOT-23-8 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:296-22675-6
ADT7468ARQZ
功能描述:板上安装温度传感器 RMT THRM CTR VLT MON RoHS:否 制造商:Omron Electronics 输出类型:Digital 配置: 准确性:+/- 1.5 C, +/- 3 C 温度阈值: 数字输出 - 总线接口:2-Wire, I2C, SMBus 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:4.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 50 C 最小工作温度:0 C 关闭: 安装风格: 封装 / 箱体: 设备功能:Temperature and Humidity Sensor
ADT7468ARQZ-REEL
功能描述:板上安装温度传感器 RMT THRM CTR VLT MON RoHS:否 制造商:Omron Electronics 输出类型:Digital 配置: 准确性:+/- 1.5 C, +/- 3 C 温度阈值: 数字输出 - 总线接口:2-Wire, I2C, SMBus 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:4.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 50 C 最小工作温度:0 C 关闭: 安装风格: 封装 / 箱体: 设备功能:Temperature and Humidity Sensor
ADT7468ARQZ-REEL7
功能描述:IC REMOTE THERMAL CTRLR 24QSOP RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 热管理 系列:dBCool® 标准包装:1 系列:- 功能:温度监控系统(传感器) 传感器类型:内部和外部 感应温度:-40°C ~ 125°C,外部传感器 精确度:±2.5°C 本地(最大值),±5°C 远程(最大值) 拓扑:ADC,比较器,寄存器库 输出类型:2 线 SMBus? 输出警报:无 输出风扇:无 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 125°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:SOT-23-8 供应商设备封装:SOT-23-8 包装:Digi-Reel® 其它名称:296-22675-6
ADT7468ARQZ-RL7
功能描述:板上安装温度传感器 RMT THRM CTR VLT MON RoHS:否 制造商:Omron Electronics 输出类型:Digital 配置: 准确性:+/- 1.5 C, +/- 3 C 温度阈值: 数字输出 - 总线接口:2-Wire, I2C, SMBus 电源电压-最大:5.5 V 电源电压-最小:4.5 V 最大工作温度:+ 50 C 最小工作温度:0 C 关闭: 安装风格: 封装 / 箱体: 设备功能:Temperature and Humidity Sensor